Generally, concentrations of substances should not be expressed in mole fractions. Formula on excess Gibbs free energy of 1 mole of solution of solute B in solvent A, for
EHL
model, assuming pure substance state as standard state, is then:
![GEm/(R·T) = xB·ln[QBA·xB/(xB+SBA·xA)]+RBA·xA·ln[(SBA·xA/(xB+SBA·xA)]-xB·ln(xB)-xA·ln(xA), where: R = gas constant; T = temperature (K); SBA = new parameter, expressing concentration of substances.](grafika/formula7.png)
From foregoing formula on logarithm of solvent A activity coefficient may be obtained:
![ln(gAA) = RBA·ln[(SBA·xA/(xB+SBA·xA)]+(RBA-SBA)·XB/(xB+SBA·xA)- ln(XA)](grafika/formula9.png)
and formula on logarithm of solute B activity coefficient may be obtained:
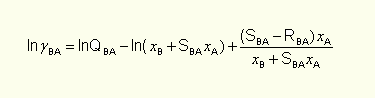
that is two-parameter equation on solvent A activity coefficient and three-parameter equation on solute B activity coefficient, leading to four parameters in the whole range of concentrations. The quantity of parameters may be reduced to two, for example advantaging of activity coefficient B in infinite dilution value.
![GEm/(R·T) = xB·ln[QBA·xB/(xB+SBA·xA)]+RBA·xA·ln[(SBA·xA/(xB+SBA·xA)]-xB·ln(xB)-xA·ln(xA), where: R = gas constant; T = temperature (K); SBA = new parameter, expressing concentration of substances.](grafika/formula7.png)
From foregoing formula on logarithm of solvent A activity coefficient may be obtained:
![ln(gAA) = RBA·ln[(SBA·xA/(xB+SBA·xA)]+(RBA-SBA)·XB/(xB+SBA·xA)- ln(XA)](grafika/formula9.png)
and formula on logarithm of solute B activity coefficient may be obtained:
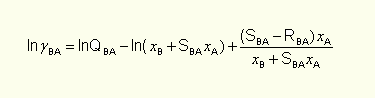
that is two-parameter equation on solvent A activity coefficient and three-parameter equation on solute B activity coefficient, leading to four parameters in the whole range of concentrations. The quantity of parameters may be reduced to two, for example advantaging of activity coefficient B in infinite dilution value.
Jump to: Top